graph_kit 0.5.1  graph_kit: ^0.5.1 copied to clipboard
graph_kit: ^0.5.1 copied to clipboard
A lightweight, in-memory graph library with pattern-based queries and efficient traversal for Dart and Flutter applications.

graph kit — lightweight typed directed multigraph + pattern queries
A tiny, in-memory, typed directed multigraph with Cypher-inspired pattern queries
A tiny, in-memory, typed directed multigraph with:
- Typed nodes (e.g.,
Person,Team,Project,Resource) - Typed edges (e.g.,
WORKS_FOR,MANAGES,ASSIGNED_TO,DEPENDS_ON) - Multiple relationships between the same nodes
- A minimal, Cypher-inspired pattern engine for traversal
See runnable examples in example/bin/ and the sample graph in example/lib/data.dart.
Table of Contents #
- Quick Preview
- Pattern Query Examples
- Mini-Cypher Reference
- Comparison with Cypher
- Core concepts
- Pattern syntax (mini, Cypher-inspired)
- Quick start
- Row-wise pattern results (new)
- Generic traversal utilities (new)
- JSON Serialization
- Examples index
- License
Quick Preview #
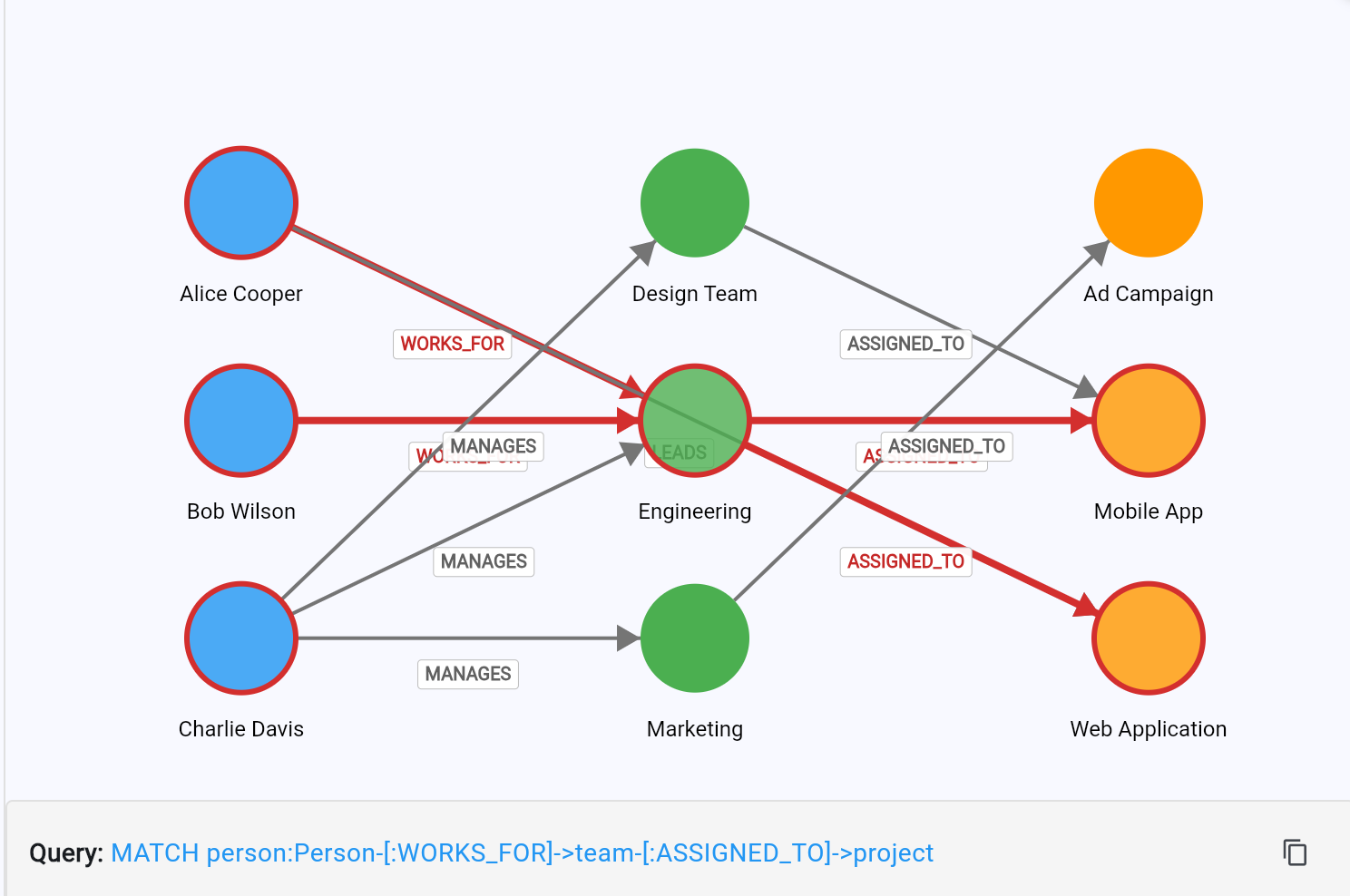
Mini-Cypher query highlighting nodes and edges in the Flutter demo.
Pattern Query Examples #
- Simple patterns:
"user:User"→{alice, bob, charlie} - Forward patterns:
"user-[:MEMBER_OF]->group" - Backward patterns:
"resource<-[:CAN_ACCESS]-group<-[:MEMBER_OF]-user"→{alice, bob} - Label filtering:
"user:User{label~Admin}"→{bob}
Mini-Cypher Reference #
Graph_kit supports a subset of Cypher syntax with some extensions. Here's the complete reference:
Keywords #
| Keyword | Support | Description |
|---|---|---|
MATCH |
Yes | Optional prefix for queries (Cypher compatibility) |
RETURN |
No | Results automatically returned as map |
WHERE |
Partial | Use {label=value} or {label~substring} instead |
Node Syntax #
variable:Type{filters}
Components:
variable: Name for results map (required) - e.g.,person,user,employee:Type: Filter by node type (optional) - e.g.,:Person,:Team{filters}: Label filtering (optional)
Node Examples:
person:Person # All Person nodes
user # All nodes (any type)
manager:Person{label=Bob} # Person nodes with exact label "Bob"
admin:User{label~Admin} # User nodes containing "Admin" in label
Edge Syntax #
-[:EDGE_TYPE]-> # Forward relationship
<-[:EDGE_TYPE]- # Backward relationship
Edge Examples:
person-[:WORKS_FOR]->team # Forward: person works for team
team<-[:WORKS_FOR]-person # Backward: people who work for team
user-[:MEMBER_OF]->group-[:CAN_ACCESS]->resource # Multi-hop
Label Filters #
| Filter | Example | Matches |
|---|---|---|
{label=Bob} |
Exact match | Node with label exactly "Bob" |
{label~bob} |
Contains (case-insensitive) | "Bob", "bob", "Bobby", "Bob Smith" |
Filter Examples:
person:Person{label=Alice Cooper} # Exact name match
user:User{label~admin} # Any admin user
team:Team{label=Engineering} # Specific team
Complete Pattern Examples #
# Basic queries (with/without MATCH)
person:Person
MATCH person:Person
# Relationships
person:Person-[:WORKS_FOR]->team:Team
MATCH person:Person-[:MANAGES]->team-[:ASSIGNED_TO]->project
# Filtered queries
person:Person{label~Alice}-[:WORKS_FOR]->team
team:Team{label=Engineering}<-[:WORKS_FOR]-person
# Multi-hop traversal
MATCH person:Person-[:WORKS_FOR]->team-[:ASSIGNED_TO]->project
Variable Names in Results #
Query results are organized by variable names:
final results = query.match('manager:Person-[:MANAGES]->team:Team');
// Returns: {'manager': {...}, 'team': {...}}
final results2 = query.match('boss:Person-[:MANAGES]->group:Team');
// Returns: {'boss': {...}, 'group': {...}}
Same node type, different roles:
owner:Person-[:OWNS]->project<-[:ASSIGNED_TO]-team<-[:WORKS_FOR]-worker:Person
# Results: {'owner': {...}, 'worker': {...}, 'project': {...}, 'team': {...}}
Syntax Limitations #
Not Supported:
- Mixed directions in single pattern:
person-[:A]->team<-[:B]-other - Variable length paths:
person-[:KNOWS*1..3]->friend - Complex WHERE clauses:
WHERE person.age > 25 - Multiple MATCH statements
- OPTIONAL MATCH
Workarounds:
- Use
matchMany()for multiple patterns - Use label filters instead of WHERE
- Use
matchRows()for path-specific results
Comparison with Cypher #
| Feature | Real Cypher | graph_kit |
|---|---|---|
| Mixed directions | Yes | No |
| Variable length paths | Yes | No |
| Optional matches | Yes | Via matchMany |
| WHERE clauses | Yes | Via label filters |
Core concepts #
- Node
- Each node has
id,type, andlabel. - Example:
u1, type=User, label=Mark.
- Each node has
- Edge types
- Relationship labels between nodes, used to traverse (e.g.,
WORKS_FOR,MANAGES).
- Relationship labels between nodes, used to traverse (e.g.,
- Graph<N extends Node>
addNode(n),addEdge(src, edgeType, dst).outNeighbors(srcId, edgeType),inNeighbors(dstId, edgeType).
- PatternQuery<N extends Node>
match(pattern, {startId})– run a single chain.matchMany([patterns], {startId})– run multiple independent chains and union results by variable name.
Pattern syntax (mini, Cypher-inspired) #
- Seeding without IDs:
alias:Type- Example:
'users:User'seeds the first segment with all nodes whosetype == 'User'.
- Example:
- Directional edges:
- Outgoing:
-[:EDGE]->(usesoutNeighbors) - Incoming:
<-[:EDGE]-(usesinNeighbors)
- Outgoing:
- Variables (aliases):
- Each segment name is a key in the returned map.
- Example:
'users:User-[:MEMBER_OF]->group'returns keys'users:User'and'group'.
Quick start #
- Build the example graph
import 'package:graph_kit/graph_kit.dart';
final g = Graph<Node>();
// Add your nodes and edges here
final pq = PatternQuery(g);
- All users (no IDs needed)
final res = pq.match('users:User');
for (final id in res['users:User'] ?? {}) {
final n = g.nodesById[id];
print('$id (${n?.type}: ${n?.label})');
}
Runnable: dart run example/bin/allusers.dart
- Users of a group (by group ID)
final res = pq.match('group-[:MEMBER_OF]<-user', startId: 'g_admins');
print(res['user']); // Set of user IDs
Runnable: dart run example/bin/group_users.dart g_admins or by label "Admins".
- Resources a person can access through their team
final res = pq.match(
'person-[:WORKS_FOR]->team-[:HAS_ACCESS]->resource',
startId: 'alice',
);
print(res['resource']); // Set of resource IDs
Runnable: dart run example/bin/user_assets.dart u1
- People who can work on a project (through team assignments)
final res = pq.match(
'project-[:ASSIGNED_TO]<-team-[:WORKS_FOR]<-person',
startId: 'web_app_project',
);
print(res['person']);
Design and performance #
- Traversal from a known ID (
startId) is fast:- Each hop uses adjacency maps; cost is proportional to the edges visited.
- Seeding by type (
alias:Type) does a one-time node scan to find initial seeds.- For small/medium graphs, this is effectively instant; indexing can be added later if needed.
matchMany([...])mirrors “multiple MATCH/OPTIONAL MATCH” lines in Cypher by running several independent chains from the same start and unioning results.
Row-wise pattern results (new) #
For cases where you need to know which variables co-occurred on the same matched path (e.g., which team gives access to which resource), use matchRows():
final rows = pq.matchRows(
'person-[:WORKS_FOR]->team-[:HAS_ACCESS]->resource',
startId: 'alice',
);
// rows: [{person: alice, team: engineering, resource: database}, ...]
// Build resource -> teams map from rows
final resourceToTeams = <String, Set<String>>{};
for (final r in rows) {
final resource = r['resource']!;
final team = r['team']!;
resourceToTeams.putIfAbsent(resource, () => <String>{}).add(team);
}
You can union multiple chains while preserving row bindings with matchRowsMany([...]):
final rows = pq.matchRowsMany([
'person-[:WORKS_FOR]->team-[:ASSIGNED_TO]->project-[:USES]->resource',
// If people can be assigned directly too:
'person-[:ASSIGNED_TO]->project-[:USES]->resource',
], startId: 'alice');
// Build resource -> projects mapping
final resourceToProjects = <String, Set<String>>{};
for (final r in rows) {
final resource = r['resource'];
final project = r['project'];
if (resource != null && project != null) {
resourceToProjects.putIfAbsent(resource, () => <String>{}).add(project);
}
}
Notes:
- The first segment supports optional
:Typeand{label=...}/{label~...}filters for seeding. - Intermediate segments currently match by structure (alias and edges); type/label filters may be added later if needed.
Generic traversal utilities (new) #
For BFS-style expansions and subgraph extraction with hop limits, use expandSubgraph from traversal.dart:
import 'package:graph_kit/graph_kit.dart';
final seeds = {'u1'};
final rightward = {'WORKS_FOR', 'ASSIGNED_TO', 'HAS_ACCESS'}; // your edge types
final sub = expandSubgraph(
g,
seeds: seeds,
edgeTypesRightward: rightward,
forwardHops: 3,
backwardHops: 0,
);
print('Nodes: ' + sub.nodes.length.toString());
print('Edges: ' + sub.edges.length.toString());
JSON Serialization #
Save and load graphs to/from JSON for persistence and data exchange:
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:graph_kit/graph_kit.dart';
// Build your graph
final graph = Graph<Node>();
graph.addNode(Node(id: 'alice', type: 'User', label: 'Alice',
properties: {'email': '[email protected]', 'active': true}));
graph.addNode(Node(id: 'team1', type: 'Team', label: 'Engineering'));
graph.addEdge('alice', 'MEMBER_OF', 'team1');
// Serialize to JSON
final json = graph.toJson();
final jsonString = graph.toJsonString(pretty: true);
// Save to file
await File('graph.json').writeAsString(jsonString);
// Load from file
final loadedJson = await File('graph.json').readAsString();
final restoredGraph = GraphSerializer.fromJsonString(loadedJson, Node.fromJson);
// Graph is fully restored - queries work immediately
final query = PatternQuery(restoredGraph);
final members = query.match('team<-[:MEMBER_OF]-user', startId: 'team1');
print(members['user']); // {alice}
Examples index #
example/bin/allusers.dart– list all usersexample/bin/group_users.dart– users in a group (by ID or by label)example/bin/user_assets.dart– assets a user can connect to
License #
See LICENSE.








