biometric_signature 9.0.0  biometric_signature: ^9.0.0 copied to clipboard
biometric_signature: ^9.0.0 copied to clipboard
Hardware-backed biometric authentication for Flutter. Create cryptographic signatures using device biometrics with keys stored in Secure Enclave/StrongBox.
biometric_signature #
Stop just unlocking the UI. Start proving the identity.
Typical biometric plugins (such as local_auth) return only a boolean indicating whether authentication succeeded.
biometric_signature goes significantly further by generating a verifiable cryptographic signature using a private key stored in hardware (Secure Enclave / StrongBox).
Even if an attacker bypasses or hooks biometric APIs, your backend will still reject the request because the attacker cannot forge a hardware-backed signature without the private key.
Features #
- Cryptographic Proof Of Identity: Hardware-backed RSA (Android) or ECDSA (all platforms) signatures that your backend can independently verify.
- Decryption Support:
- RSA: RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding (Android native, iOS/macOS via wrapped software key)
- EC: ECIES (
eciesEncryptionStandardX963SHA256AESGCM)
- Hardware Security: Uses Secure Enclave (iOS/macOS) and Keystore/StrongBox (Android).
- Hybrid Architectures:
- Android Hybrid EC: Hardware EC signing + software ECIES decryption. Software EC private key is AES-wrapped using a Keystore/StrongBox AES-256 master key that requires biometric authentication for every unwrap.
- iOS/macOS Hybrid RSA: Software RSA key for both signing and decryption, wrapped using ECIES with Secure Enclave EC public key. Hardware EC is only used for wrapping/unwrapping.
- Key Invalidation: Keys can be bound to biometric enrollment state (fingerprint/Face ID changes).
- Device Credentials: Optional PIN/Pattern/Password fallback on Android.
Security Architecture #
Key Modes #
The plugin supports different operational modes depending on the platform:
Android
Android supports three key modes:
-
RSA Mode (
SignatureType.rsa):- Hardware-backed RSA-2048 signing (Keystore/StrongBox)
- Optional RSA decryption (PKCS#1 padding)
- Private key never leaves secure hardware
-
EC Signing-Only (
SignatureType.ecdsa,enableDecryption: false):- Hardware-backed P-256 key in Keystore/StrongBox
- ECDSA signing only
- No decryption support
-
Hybrid EC Mode (
SignatureType.ecdsa,enableDecryption: true):- Hardware EC key for signing
- Software EC key for ECIES decryption
- Software EC private key encrypted using AES-256 GCM master key (Keystore/StrongBox)
- Per-operation biometric authentication required for decryption
iOS / macOS
Apple platforms support two key modes (Secure Enclave only supports EC keys natively):
-
EC Mode (
SignatureType.ecdsa):- Hardware-backed P-256 key in Secure Enclave
- ECDSA signing
- Native ECIES decryption (
eciesEncryptionStandardX963SHA256AESGCM) - Single key for both operations
-
RSA Mode (
SignatureType.rsa) - Hybrid Architecture:- Software RSA-2048 key for both signing and decryption
- RSA private key wrapped using ECIES with Secure Enclave EC public key
- Hardware EC key is only used for wrapping/unwrapping the RSA key
- Wrapped RSA key stored in Keychain as
kSecClassGenericPassword - Per-operation biometric authentication required to unwrap RSA key
Workflow Overview #
-
Enrollment
User authenticates → hardware generates a signing key.
Hybrid modes additionally generate a software decryption key, which is then encrypted using secure hardware.
-
Signing
Biometric prompt is shown
Hardware unlocks the signing key, and a verifiable signature is produced.
-
Decryption
A biometric prompt is shown again.
Hybrid modes unwrap the software private key using hardware-protected AES-GCM, then decrypt the payload.
-
Backend Verification
The backend verifies signatures using the registered public key.
Verification must not be performed on the client.
Backend Verification #
Perform verification on the server. Below are reference implementations.
Node.js #
const crypto = require('crypto');
function verifySignature(publicKeyPem, payload, signatureBase64) {
const verify = crypto.createVerify('SHA256');
verify.update(payload); // The original string you sent to the plugin
verify.end();
// Returns true if valid
return verify.verify(publicKeyPem, Buffer.from(signatureBase64, 'base64'));
}
Python #
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import padding
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import serialization
import base64
def verify_signature(public_key_pem_str, payload_str, signature_base64_str):
public_key = serialization.load_pem_public_key(public_key_pem_str.encode())
signature = base64.b64decode(signature_base64_str)
try:
# Assuming RSA (For EC, use ec.ECDSA(hashes.SHA256()))
public_key.verify(
signature,
payload_str.encode(),
padding.PKCS1v15(),
hashes.SHA256()
)
return True
except Exception:
return False
Go #
import (
"crypto"
"crypto/rsa"
"crypto/sha256"
"crypto/x509"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/pem"
"fmt"
)
func verify(pubPemStr, payload, sigBase64 string) error {
block, _ := pem.Decode([]byte(pubPemStr))
pub, _ := x509.ParsePKIXPublicKey(block.Bytes)
rsaPub := pub.(*rsa.PublicKey)
hashed := sha256.Sum256([]byte(payload))
sig, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(sigBase64)
return rsa.VerifyPKCS1v15(rsaPub, crypto.SHA256, hashed[:], sig)
}
Getting Started #
To get started with Biometric Signature, follow these steps:
- Add the package to your project by including it in your
pubspec.yamlfile:
dependencies:
biometric_signature: ^9.0.0
| Android | iOS | macOS | Windows | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Support | SDK 24+ | 13.0+ | 10.15+ | 10+ |
iOS Integration #
This plugin works with Touch ID or Face ID. To use Face ID in available devices, you need to add:
<dict>
<key>NSFaceIDUsageDescription</key>
<string>This app is using FaceID for authentication</string>
</dict>
to your Info.plist file.
Android Integration #
Activity Changes
This plugin requires the use of a FragmentActivity instead of Activity. Update your MainActivity.kt to extend FlutterFragmentActivity:
import io.flutter.embedding.android.FlutterFragmentActivity
class MainActivity : FlutterFragmentActivity() {
}
Permissions
Update your project's AndroidManifest.xml file to include the
USE_BIOMETRIC permission.
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.app">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.USE_BIOMETRIC" />
</manifest>
macOS Integration #
This plugin works with Touch ID on supported Macs. To use Touch ID, you need to:
- Add the required entitlements to your macOS app.
Open your macOS project's entitlements file (typically located at macos/Runner/DebugProfile.entitlements and macos/Runner/Release.entitlements) and ensure it includes:
<key>com.apple.security.device.usb</key>
<false/>
<key>com.apple.security.device.bluetooth</key>
<false/>
<key>keychain-access-groups</key>
<array>
<string>$(AppIdentifierPrefix)com.yourdomain.yourapp</string>
</array>
Replace com.yourdomain.yourapp with your actual bundle identifier.
- Ensure CocoaPods is properly configured in your
macos/Podfile. The plugin requires macOS 10.15 or later:
platform :osx, '10.15'
Windows Integration #
This plugin uses Windows Hello for biometric authentication on Windows 10 and later.
Platform Limitations:
- Windows only supports RSA keys (ECDSA is ignored)
- Windows Hello always authenticates during key creation (
enforceBiometricis effectively alwaystrue) setInvalidatedByBiometricEnrollmentanduseDeviceCredentialsare ignored- Decryption is not supported on Windows
No additional configuration is required. The plugin will automatically use Windows Hello when available.
Common Setup #
- Import the package in your Dart code:
import 'package:biometric_signature/biometric_signature.dart';
- Initialize the Biometric Signature instance:
final biometricSignature = BiometricSignature();
Usage #
This package simplifies server authentication using biometrics. The following image from Android Developers Blog illustrates the basic use case:
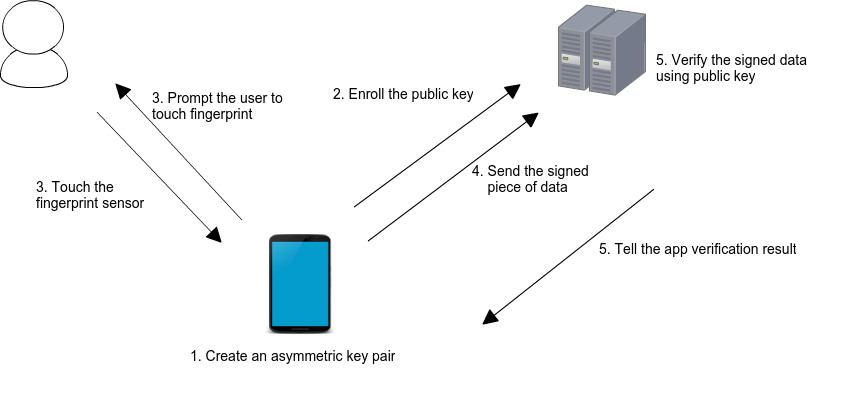
When a user enrolls in biometrics, a key pair is generated. The private key is securely stored on the device, while the public key is sent to a server for registration. To authenticate, the user is prompted to use their biometrics, unlocking the private key. A cryptographic signature is then generated and sent to the server for verification. If the server successfully verifies the signature, it returns an appropriate response, authorizing the user.
Class: BiometricSignaturePlugin #
This class provides methods to manage and utilize biometric authentication for secure server interactions. It supports both Android and iOS platforms.
createKeys({ config, keyFormat, promptMessage }) #
Generates a new key pair (RSA 2048 or EC) for biometric authentication. The private key is securely stored on the device.
-
Parameters:
config:CreateKeysConfigwith platform options (see below)keyFormat: Output format (KeyFormat.base64,pem,hex)promptMessage: Custom authentication prompt message
-
Returns:
Future<KeyCreationResult>.publicKey: The formatted public key string (Base64 or PEM).code:BiometricErrorcode (e.g.,success,userCanceled).error: Descriptive error message.
CreateKeysConfig Options
| Option | Platforms | Description |
|---|---|---|
signatureType |
Android/iOS/macOS | SignatureType.rsa or SignatureType.ecdsa |
enforceBiometric |
Android/iOS/macOS | Require biometric during key creation |
setInvalidatedByBiometricEnrollment |
Android/iOS/macOS | Invalidate key on biometric changes |
useDeviceCredentials |
Android/iOS/macOS | Allow PIN/passcode fallback |
enableDecryption |
Android | Enable decryption capability |
promptSubtitle |
Android | Subtitle for biometric prompt |
promptDescription |
Android | Description for biometric prompt |
cancelButtonText |
Android | Cancel button text |
final result = await biometricSignature.createKeys(
keyFormat: KeyFormat.pem,
promptMessage: 'Authenticate to create keys',
config: CreateKeysConfig(
signatureType: SignatureType.rsa,
enforceBiometric: true,
setInvalidatedByBiometricEnrollment: true,
useDeviceCredentials: false,
enableDecryption: true, // Android only
),
);
if (result.code == BiometricError.success) {
print('Public Key: ${result.publicKey}');
}
createSignature({ payload, config, signatureFormat, keyFormat, promptMessage }) #
Prompts the user for biometric authentication and generates a cryptographic signature.
- Parameters:
payload: The data to signconfig:CreateSignatureConfigwith platform optionssignatureFormat: Output format for signaturekeyFormat: Output format for public keypromptMessage: Custom authentication prompt
CreateSignatureConfig Options
| Option | Platforms | Description |
|---|---|---|
allowDeviceCredentials |
Android | Allow PIN/pattern fallback |
promptSubtitle |
Android | Subtitle for biometric prompt |
promptDescription |
Android | Description for biometric prompt |
cancelButtonText |
Android | Cancel button text |
shouldMigrate |
iOS | Migrate from legacy keychain storage |
- Returns:
Future<SignatureResult>.signature: The signed payload.publicKey: The public key.code:BiometricErrorcode.
final result = await biometricSignature.createSignature(
payload: 'Data to sign',
promptMessage: 'Please authenticate',
signatureFormat: SignatureFormat.base64,
keyFormat: KeyFormat.base64,
config: CreateSignatureConfig(
allowDeviceCredentials: false,
),
);
decrypt({ payload, payloadFormat, config, promptMessage }) #
Decrypts the given payload using the private key and biometrics.
- Parameters:
payload: The encrypted datapayloadFormat: Format of encrypted data (PayloadFormat.base64,hex)config:DecryptConfigwith platform optionspromptMessage: Custom authentication prompt
DecryptConfig Options
| Option | Platforms | Description |
|---|---|---|
allowDeviceCredentials |
Android | Allow PIN/pattern fallback |
promptSubtitle |
Android | Subtitle for biometric prompt |
promptDescription |
Android | Description for biometric prompt |
cancelButtonText |
Android | Cancel button text |
shouldMigrate |
iOS | Migrate from legacy keychain storage |
Note: Decryption is not supported on Windows.
- Returns:
Future<DecryptResult>.decryptedData: The plaintext string.code:BiometricErrorcode.
final result = await biometricSignature.decrypt(
payload: encryptedBase64,
payloadFormat: PayloadFormat.base64,
promptMessage: 'Authenticate to decrypt',
config: DecryptConfig(
allowDeviceCredentials: false,
),
);
deleteKeys() #
Deletes all biometric key material (signing and decryption keys) from the device's secure storage.
- Returns:
Future<bool>.true: Keys were successfully deleted, or no keys existed (idempotent).false: Deletion failed due to a system error.
Note: This operation is idempotent—calling
deleteKeys()when no keys exist will still returntrue. This allows safe "logout" or "reset" flows without checking key existence first.
final deleted = await biometricSignature.deleteKeys();
if (deleted) {
print('All biometric keys removed');
}
biometricAuthAvailable() #
Checks if biometric authentication is available on the device and returns a structured response.
- Returns:
Future<BiometricAvailability>.canAuthenticate:boolindicating if auth is possible.hasEnrolledBiometrics:boolindicating if user has enrolled biometrics.availableBiometrics:List<BiometricType>(e.g.,fingerprint,face).reason: String explanation if unavailable.
final availability = await biometricSignature.biometricAuthAvailable();
if (availability.canAuthenticate) {
print('Biometrics available: ${availability.availableBiometrics}');
} else {
print('Not available: ${availability.reason}');
}
getKeyInfo({ checkValidity, keyFormat }) #
Retrieves detailed information about existing biometric keys without prompting for authentication.
- Parameters:
checkValidity: Whether to verify the key hasn't been invalidated by biometric changes. Default isfalse.keyFormat: Output format for public keys (KeyFormat.base64,pem,hex). Default isbase64.
- Returns:
Future<KeyInfo>.exists: Whether any biometric key exists.isValid: Key validity status (only populated whencheckValidity: true).algorithm:"RSA"or"EC".keySize: Key size in bits (e.g., 2048, 256).isHybridMode: Whether using hybrid signing/decryption keys.publicKey: The signing public key.decryptingPublicKey: Decryption key (hybrid mode only).
final info = await biometricSignature.getKeyInfo(
checkValidity: true,
keyFormat: KeyFormat.pem,
);
if (info.exists && (info.isValid ?? true)) {
print('Algorithm: ${info.algorithm}, Size: ${info.keySize}');
print('Hybrid Mode: ${info.isHybridMode}');
}
biometricKeyExists({ checkValidity }) #
Convenience method that wraps getKeyInfo() and returns a simple boolean.
- Parameters:
checkValidity: Whether to check key validity. Default isfalse.
- Returns:
Future<bool>-trueif key exists and is valid.
final exists = await biometricSignature.biometricKeyExists(checkValidity: true);