amity_sdk 0.0.1-gazelle.1  amity_sdk: ^0.0.1-gazelle.1 copied to clipboard
amity_sdk: ^0.0.1-gazelle.1 copied to clipboard
The SDK that enables social features such as Feeds, Groups, Profiles, Content Posts, and Social Media Type Interactions
Amity-Social-Cloud-SDK-Flutter #
Git tag convention #
- Use Semantic Versioning.
Architecture Overview #
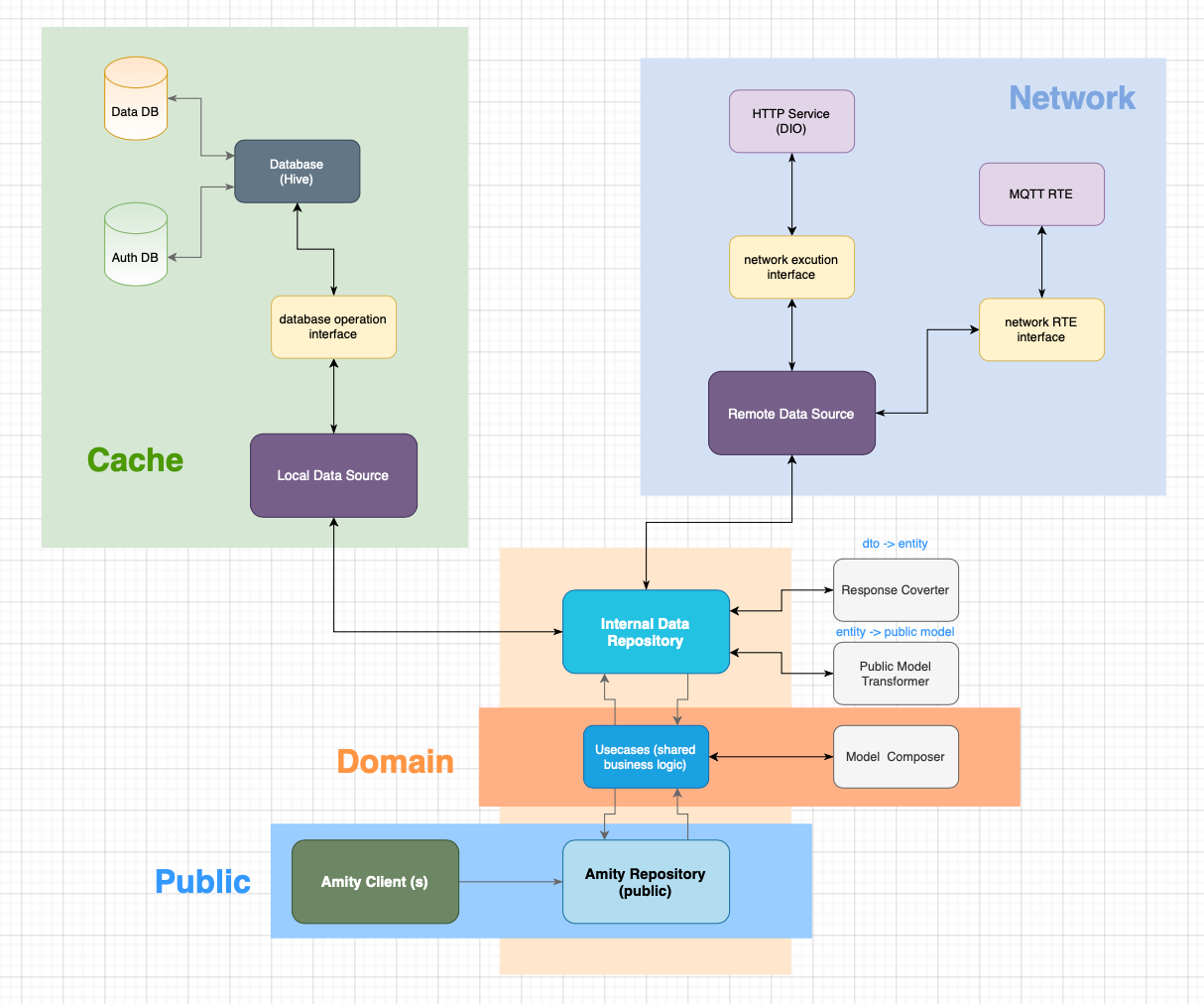
Architecture Interaction #
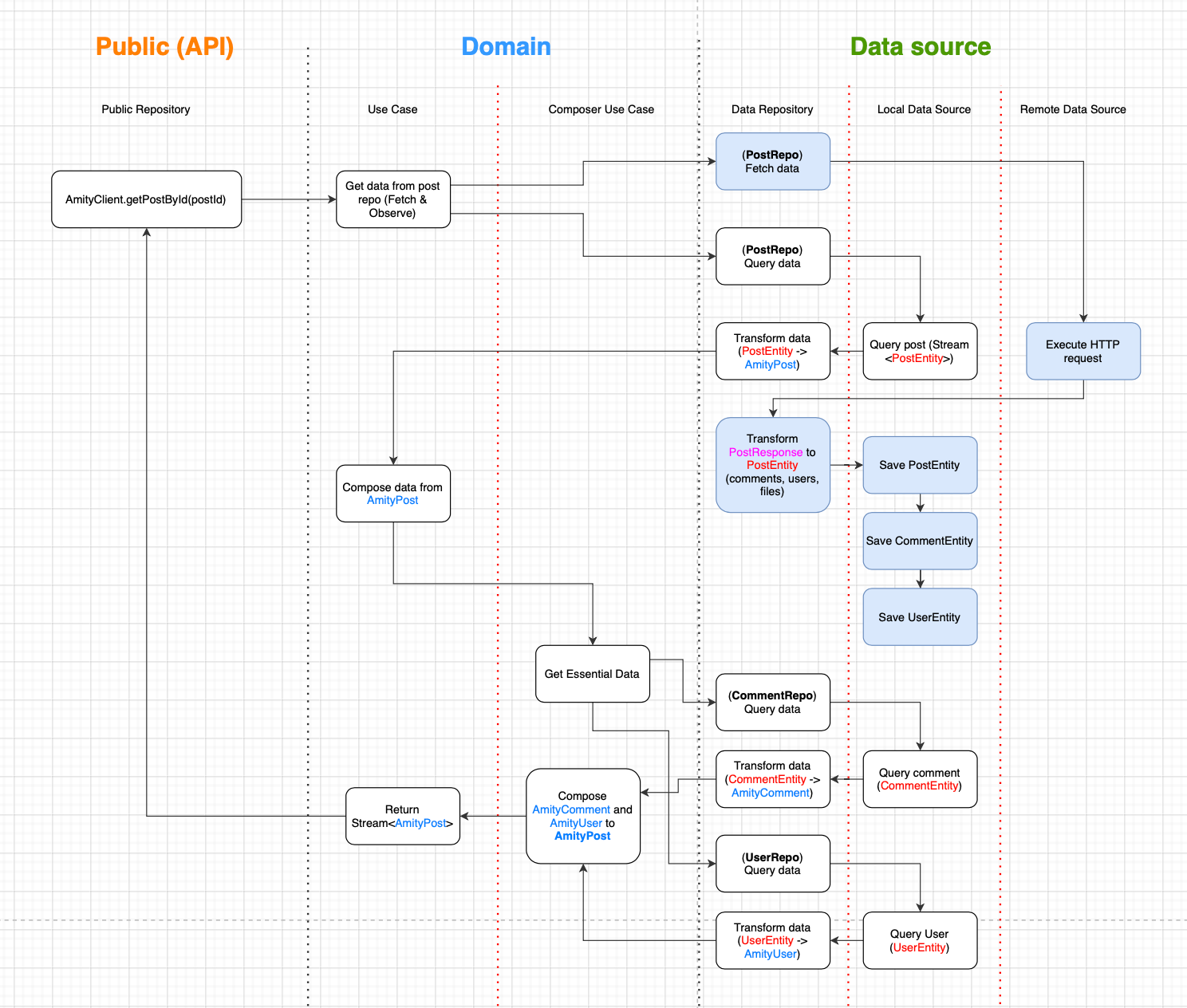
Unit testing #
(A) Test Components #
There are always two type of components in a test.
- The System Under Test (SUT) refers to a system that is being tested for correct operation (what do we want to test, for example, Use Cases and Repositories).
- Depended On Component (DOC), is a collaborator, component that is required by SUT to fulfill its duties (SUT's repositories).
- Easy collaborations.
- Awkward collaborations.
(B) Test Structure #
A test always includes 4 main parts.
- Setup
- Data setup.
- Expections setup.
- Exercise
- Verify
- Data Verification.
- Expections Verification.
- Tear down
- Explicit Teardown.
- Implicit Teardown (GB).
(C) Test Doubles #
Any kind of pretended objects used in place of a real object for testing purpose.
Dummy objects (with data verification)
Objects are passed around but never actually used, usually they are just used to fill parameters, let a test runs, can be as simple as null.
Fake objects (with data verification)
Objects actually have working implementations, but usually take some shortcut which makes them not suitable for production, simplify an implementation of a test by removing unnecessary or heavyweight dependencies, an in-memory database is a good example.
Stubs (with data verification)
Similar to Fakes but provide simplest answers or hard-coded to let a test runs regardless of an input, it won’t fail the test, we don’t care what happens inside, implement dependencies (stubbed code), not doing anything outside of the test
Mocks (used with expection verification)
Pre-programmed objects with expectation, something that runs a fake business logic instead of a real one. Similar to Stubs but we don’t expect from Mocks to do anything, but to assure that a specific order of method calls are made.
Spies (can be used with both data and expection verifications)
Are Stubs that wrap a real object inside, basically the real object with methods shadowed by stub methods (block real methods from being called). Non-stubbed methods are just rooted through to the original object.
(D) Test Styles #
Classical Style
The classical style is to use real objects if possible and a double if it's awkward to use the real thing. The kind of double doesn't really matter that much.
Facts
Test Isolation
- A buggy System under test is being used as a collaborator for other tests which leads to other failures. As a result of highly used causes a ripple of failing tests all across the system, it results in a lot of debugging in order to find a root of an error
- Multiple real objects can be much harder to find a real source of a bug
- It’s not important to test units and integration separately, if we can achieve the same in one set of tests. Because the most reliable tests go through all the layers, we start from end-to-end tests (outside-in).
Test Reliability
- It is not just unit tests, but also mini-integration tests as we mimic real implementation.
Test Coupling
- Only care about the final state not how it was delivered which is something we choose on the testing state.
Mockist Style
A mockist tester will always use a mock for any object with interesting behavior.
Facts
Test Isolation
- A buggy System under test can be found easily.
- Tests aren’t dependent on code that isn’t under test, The goal is gaining the ability to change or remove one part of the code, without having to change the tests in other parts.
Test Reliability
- It loses mini-integration tests ability, and runs to a risk of incorrect expectations.
Test Coupling
- Test outbound calls of a system under test to ensure it talks properly to its collaborations, more coupled to implementation, changing the nature of calls to collaborations usually cause a test to break.
Amity Stype
There is one style that fits all applications perfectly, both Classical and Mockist have Pros and Cons, and we are trying to balance them. Even though Mockist seem to fit with the current SDK's architecture than Classical (based on the team's desicion on 5/1/2022) we all agree that there is no need to mock everything beside a SUT, if it is really straightforward and easy to construct/instantiate so we gain one of benefits in using Classical by using a real object.
(E) System components (App components) #
First, remember that everything in your system (App) is either a Service, Entity or Value. Never mock values, sometime mock entities, but mock services freely.
⚠️ mock is a pretty common verb for substituting a test double, there are sevarals type of test doubles.
Value
A value has no lifecycle, usually immutable, “equals” () depends on the value. For example, a constant value and a data type.
Entity
A entity has lifecylce, usually persisted, “equals” () depends on the id. That means two objects can look the same but aren't equal. For example, a data model.
Service
A service provides API for applications to use it. A service is transient, can be pluggable and is often best when stateless. The notion of equality doesn’t much make sense for a service, and in many applications, one instance of a service is enough. For example, Room, Restrofit and OkHttp client.
(F) Importance Notes! #
- SUT is always be a real object.
- Only test where logics are located (based on the team's desicion on 6/1/2022).
- DO NOT mock third party libraries, mock its interface, create one if it doesn't exist.
⚠️ mock is a pretty common verb for substituting a test double, there are sevarals type of test doubles.
(G) Example #
When I feel like it :P